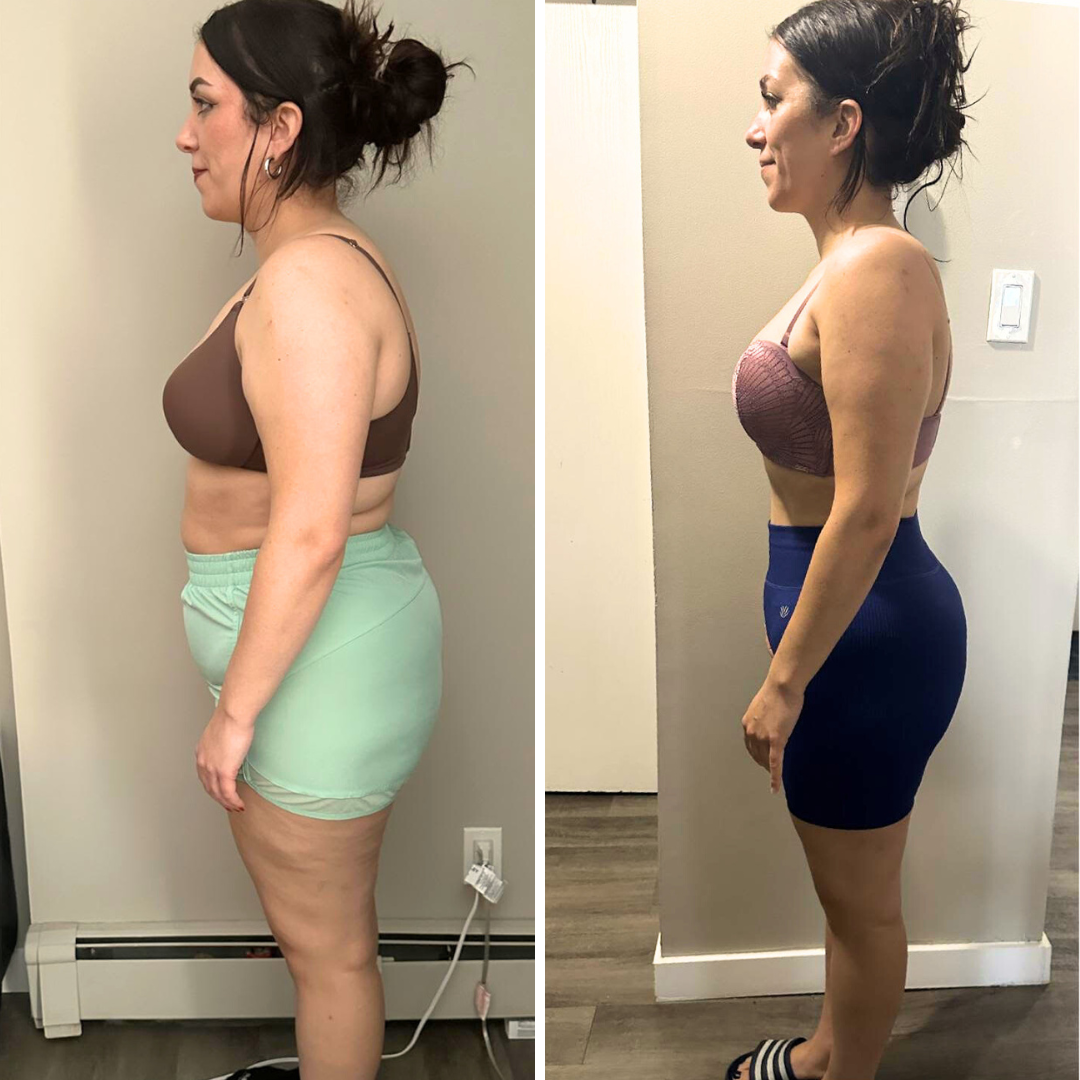
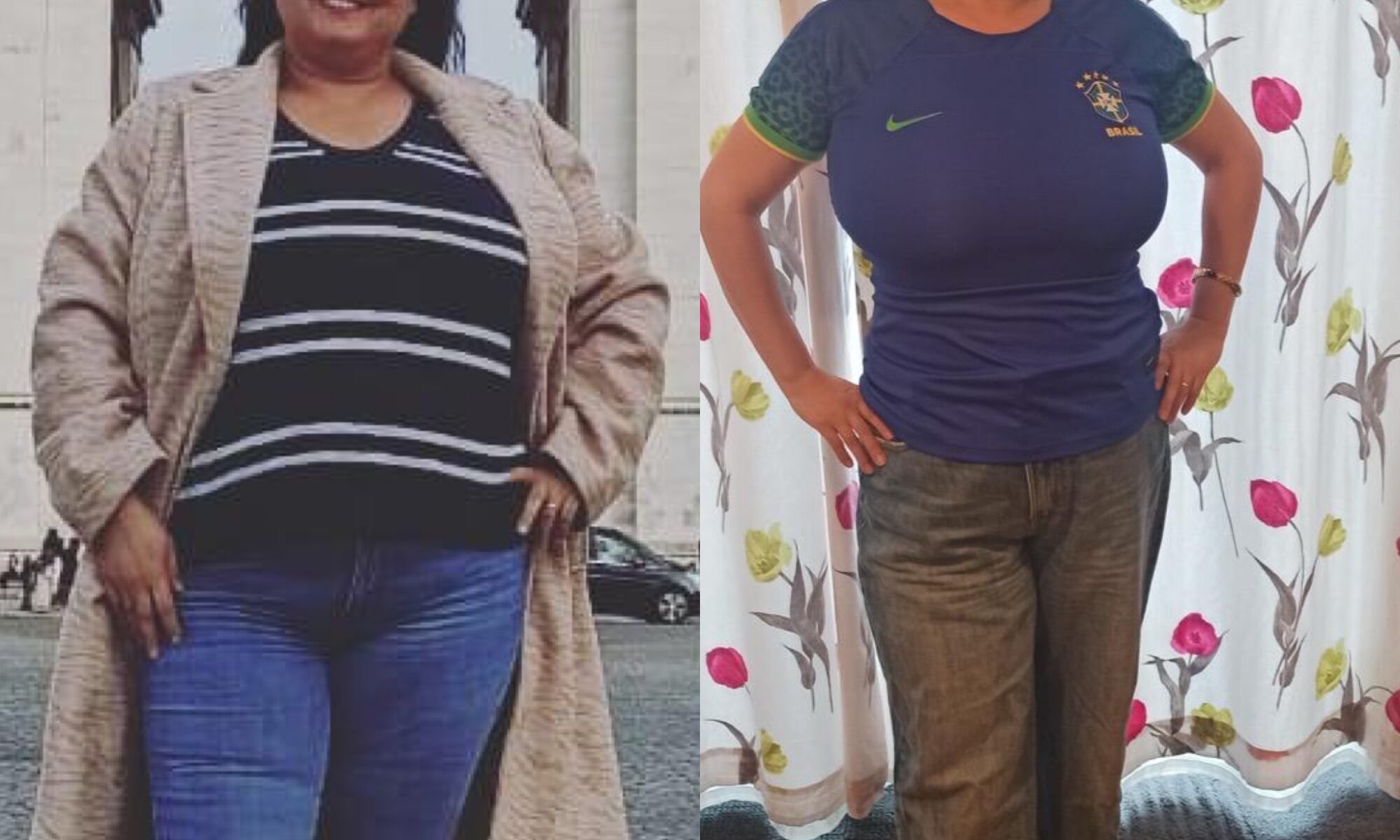
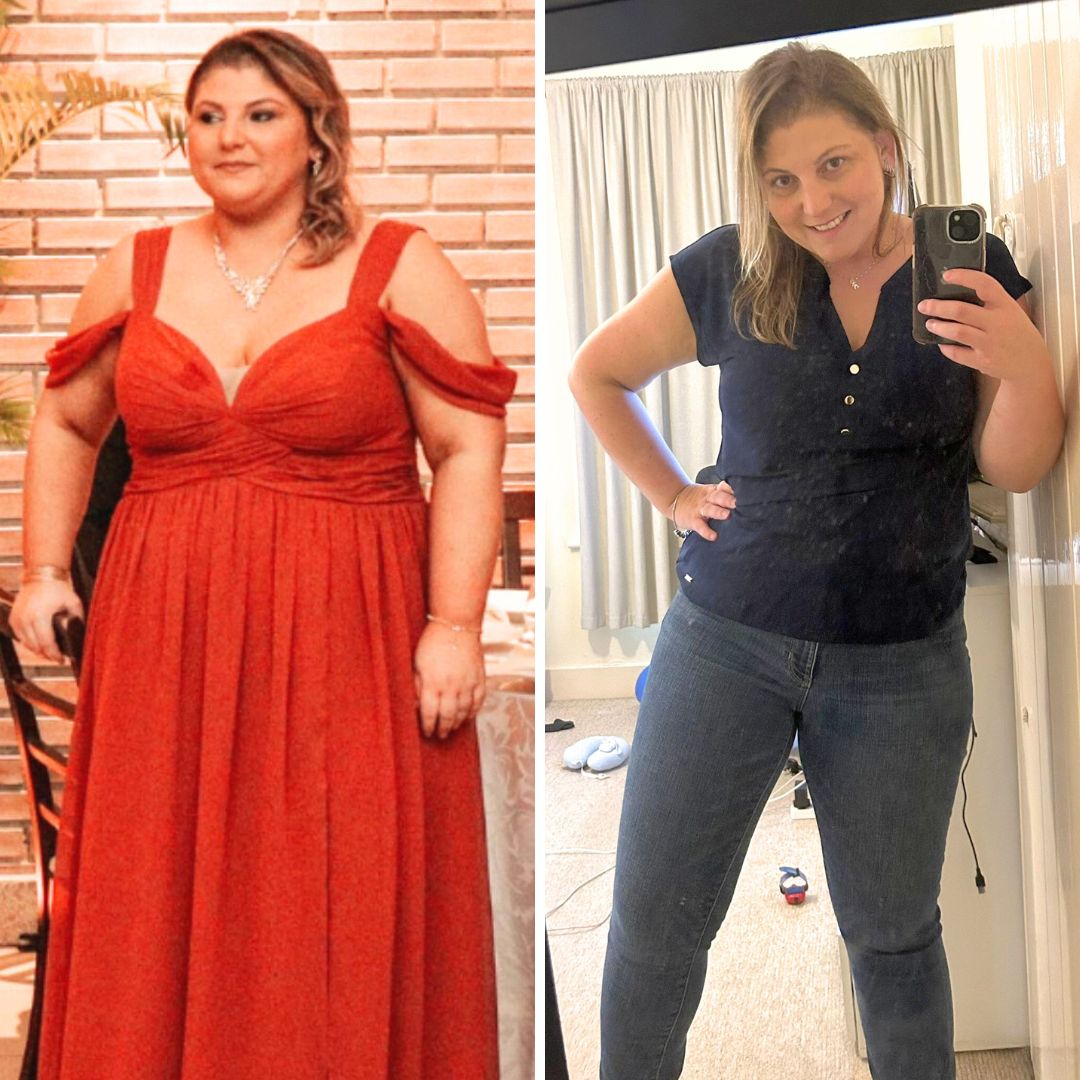
If you are looking for help to lose weight, stay here and read until the end to find out how a dietitian helped someone to lose 25kg in 5 months.
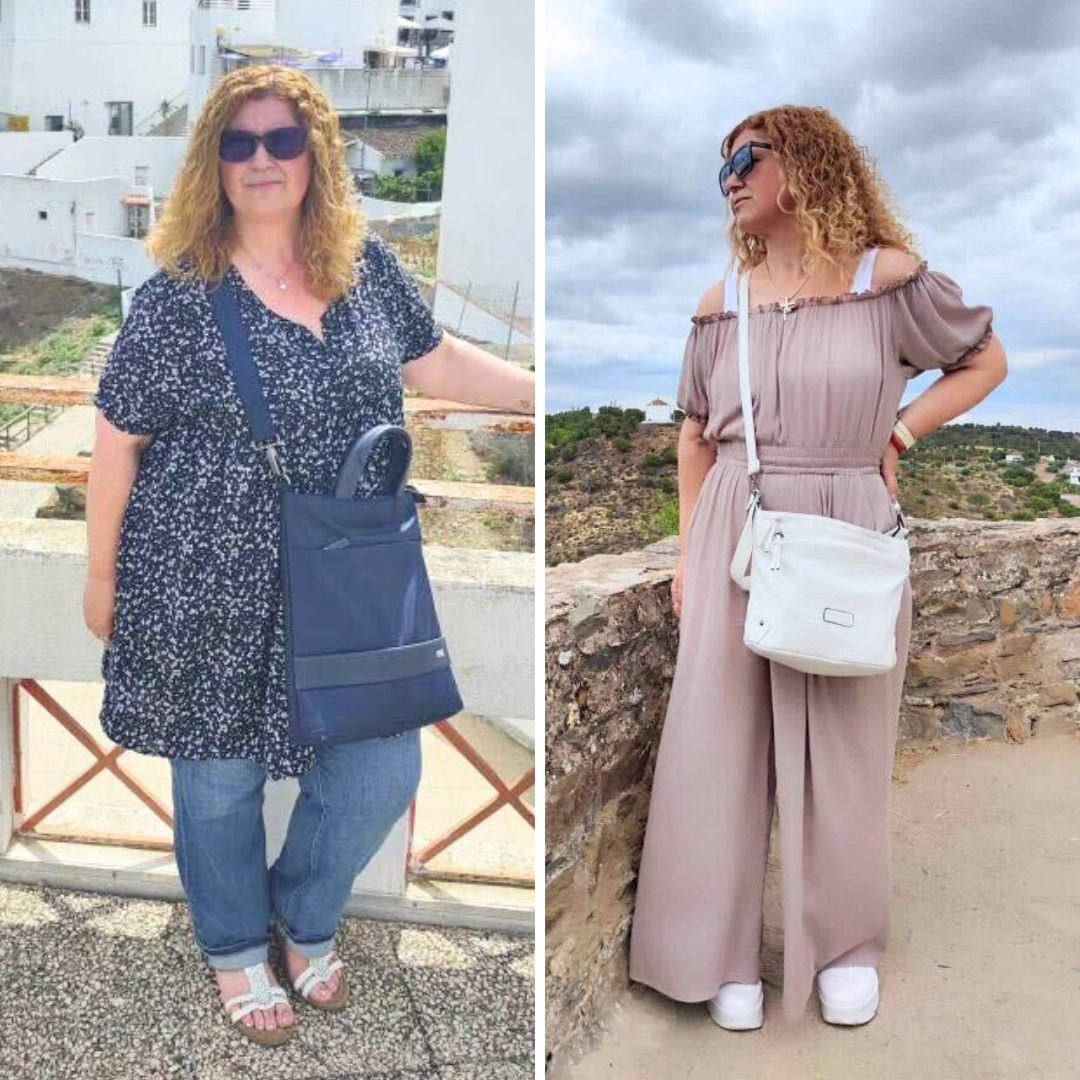
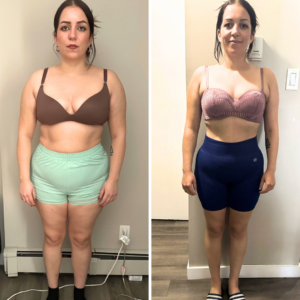
Meet Barbara Moniz, who lives in Canada and achieved her weight loss goals through online dietitian consultations at Raquel Britzke Clinic. Barbara successfully lost 26kg in 5 months with personalised care and direct support from her dietitian throughout the process.
Barbara joined the Transform360 weight loss programme, designed for men and women aiming to lose 20kg or more in six months. The programme includes monthly consultations with a private dietitian from Raquel’s team and a supportive WhatsApp group where participants interact and help each other along the way. However, you can achieve weight loss purely by doing monthly weight loss consultations either in the clinic in London or doing it online.
Not only did Barbara transform her body, but she also experienced a significant boost in energy levels for daily activities, eliminated leg and back pain, and gained much more confidence.
Why did you seek help from a dietitian to lose weight?
“At the start of the year, I felt frustrated, very heavy, and lacked energy for anything. I knew I needed to make a change.
But I was also tired of trying countless diets that didn’t work. I have been following Raquel’s work on Instagram and Facebook for 12 years, and I’m a big fan. When Raquel announced the opening of a new Transform360 group, I decided to sign up. I was confident it would work, as I’d seen so many testimonials and feedback from other patients.”
How was the weight loss process and your online consultations with the dietitian?
Barbara followed the diet plan strictly and lost 20kg within the first three months. “That gave me so much motivation to keep going,” she shared.
“In addition to sticking closely to the diet, I exercise 3–4 times a week because I want to tone my body and gain muscle definition. My dietitian is incredibly attentive and always available to answer my questions.
The monthly one-hour consultations are amazing, as I can clarify all my doubts. Even between consultations, I had support, and my dietitian always checked on me and asked about my progress. This level of care and guidance ensured I stayed on track with clear and achievable goals—without crazy diets or attempting it alone, making mistakes, and getting frustrated.
Having a qualified specialist in weight loss and personalised consultations made all the difference in my journey.”
What were the diets like over these six months?
“Each month, the diet strategy changes to stimulate the metabolism for further weight loss. Calorie intake is tailored to each patient’s metabolism, dietary preferences, and lifestyle.
Each month involved a specific approach, such as detox, low-carb, or Mediterranean diets. The meal plans were detailed, including timings, portion sizes, and combinations of foods. The foods were accessible and easy to find regardless of where you live.
We also had access to a substitution list and a healthy recipe book for more alternatives when needed.”
How else can the dietitian can help beyond weight loss?
Barbara shared, “I’m focused on losing weight because I know that healthy eating and reaching a healthy weight will improve my fertility and lead to a healthier pregnancy.”
“I had tried losing weight in the past without success, mainly due to inconsistency and a lack of motivation and support—something I now have thanks to this programme.”
What has changed in your life now that you’ve lost 26kg?
“My family keeps complimenting me and asking, ‘Wow! What did you do?’
Even my boyfriend has lost 7kg just by following the lifestyle changes I made at home—imagine if he had a personalised plan for himself!
Before, I used to have a lot of knee and back pain, but all that changed with the weight loss.
My confidence and self-esteem have improved drastically. I looked at myself in the mirror and decided I didn’t want to stay the same. I had to change. Today, I’m amazed at how far I’ve come, and my self-belief has grown so much.
The clinic provides a lot of support, which helps immensely. I watched the videos and resources they shared, which motivated me to stay on track and believe in myself.”
Barbara, if you could pick one thing you liked most about the programme, what would it be?
“I liked everything, but the meal plans were my favourite because they were completely personalised to my preferences.”
What would you say to people hesitant about starting or sticking to a diet?
“First, it’s an investment—but it’s an investment in your health, and that’s priceless. You have to want to change, and the Raquel Britzke Clinic is the best option to help you achieve that because of their experience and support.
It’s not easy, but you can’t give up. You need to want it and commit to it. I now have so much energy and get so much done both at home and outside.
Most importantly, you have to change your mindset. There’s no point in losing weight if you keep the same unhealthy mentality—it will only lead to regaining the weight. Changing my way of thinking towards eating and food choices were the biggest transformations I’ve made.”
If Barbara’s story inspired you, or if you or someone you know needs help to transform their body and health, book a dietitian consultation at our clinic—online or in person in central London. Benefit from personalised care and attention to help you achieve your goals and maintain them for life. Lose weight with the help of a dietitian for lasting results. Book your consultation by clicking here.















